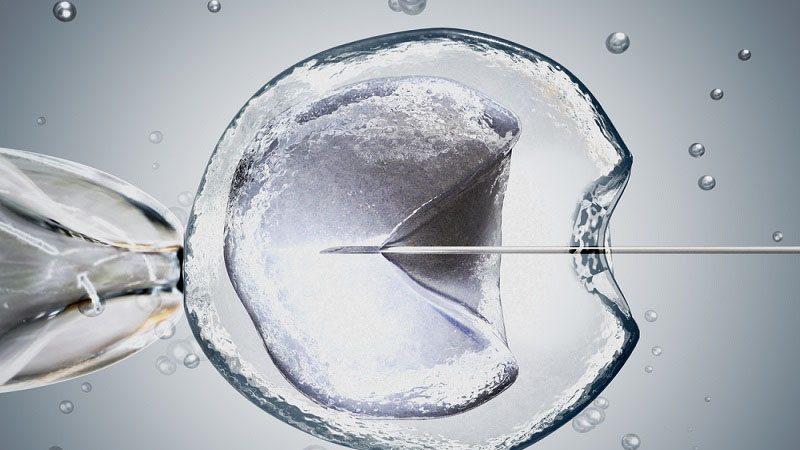
Cryopreservation is the method of artificially extending the fertility age of a woman by extracting and freezing the unfertilized eggs from a woman’s ovary. The maximum legal preservation period is ten years as proposed by the HFEA (Human Fertilisation and Embryology Authority). As the experimental stage is over so many women are opting to freeze their eggs due to various personal and professional reasons.
Methods Used for Freezing Eggs
Currently, two different processes are largely utilized by Reproductive Endocrinologists to freeze oocytes or unfertilized human eggs. Vitrification and the conventional are the two processes for slow-freeze method. It's been over three decades that the slow-freeze method is being utilized to freeze embryos. However, until recently, the slow-freeze method was found to be unreliable and troublesome in favourably replicating the results for unfertilized eggs.
Egg Freezing Using the Vitrification (Flash Freeze) Method
In this, the eggs are exposed for absolute critical time to many different solutions for the number of different respective exposure times. The margin of error is very little as the solutions are extremely concentrated and potentially toxic to the eggs. This procedure must be performed with accuracy and precision, requiring special skills and concentration by the embryologist.
Slow Freezing
One of the most commonly used processes worldwide is slow freezing. In this, the cells (eggs or oocytes) are cooled in steps under -196 Celsius, this temperature is controlled through a computer. Also, a cryoprotective agent is released for the protection of eggs. This results in prolonged cell storage as the biological processes in the cell are shut down. Besides the cryoprotective agents (anti-freeze media) prevent osmotic damage in the cell as far as possible. Furthermore, they do not prevent the formation of ice, which can damage the cell organelles.
Why Freeze Eggs?
Limited amount of eggs produced: Each woman is born with a finite number of eggs that steadily declines as she ages. Irrespective of the amount of primary ovarian reserve, the most favourable chances for women are always in their 20's as eggs are healthy. For women in their 30s, pregnancy chances decline, from 25 percent throughout their 20's to 15 percent during 30's and eventually drops to 5 percent as they enter their 40s.
Quality of eggs reduces over time: As you age, your egg quality diminishes. As the probability of conception declines each month, the likelihood of having eggs with chromosomal abnormalities also increases and so does the chances of miscarriage. Egg freezing helps in preserving the current health of eggs and by this, it increases the chances of conception through IVF in the future.
The peace of mind regarding motherhood and career goals: Egg freezing puts women on the same playing field with men, whose biological clock may not tick as loudly, per se. The process will allow you to find a secure relationship, focus on your professional goals, and ultimately take control of your life by giving you a choice to get pregnant when the time is right, for you.
Low risk for pregnancies during advanced age: Social egg freezing, followed by in vitro fertilization (IVF) and embryo transfer, offers two important benefits to women who anticipate becoming pregnant at an advanced age: it provides them with the possibility of becoming a genetic parent using their frozen-thawed eggs, and it reduces the risk of having children with chromosomal abnormalities associated with ovarian aneuploidy.
Egg freezing carries various risks, including:
- Conditions related to the use of fertility drugs. Rarely, use of injectable fertility drugs to induce ovulation, ovaries might get swollen and bit painful after ovulation or egg retrieval. Signs and symptoms include abdominal pain, bloating, nausea, vomiting and diarrhoea. There's a rarer possibility of developing a more severe and life-threatening syndrome.
- Another very rare but having a considerate risk is of bleeding, infection or damage to the bowel, bladder or a blood vessel because of using an aspirating needle to retrieve eggs.
- Egg freezing provides hope for a future pregnancy, but there's no guarantee of success so this is an emotional risk.
Success Rates of Egg Freezing
Before discussing success rates we will like to share the fact that egg freezing is a new procedure, so the number of cases of IVF or any other method of conception through these frozen eggs is very small. However, the success rate for such women is good, but always remember that the success in IVF is considerately dependant on the woman’s age. Note: Here success rate means the good quality of eggs after preserving and developing embryo after successful plantation.
The main goal behind doing all this is bringing home a healthy baby, so the birth rates are also considered in the success rate. 2% to 12% success rate is common in older methods of egg retrieving and IVF, whereas for egg freezing method 4% to 14% is the success rate.



 IVF Centers
IVF Centers IVF Doctors
IVF Doctors Joint Replacement
Joint Replacement Spine Surgeries
Spine Surgeries Dental
Dental Slimming/Weight Loss Clinics
Slimming/Weight Loss Clinics Hair Transplant Clinics
Hair Transplant Clinics Physiotherapy clinics
Physiotherapy clinics
 Search
Search